Juan Brignardello Vela
Juan Brignardello, asesor de seguros, se especializa en brindar asesoramiento y gestión comercial en el ámbito de seguros y reclamaciones por siniestros para destacadas empresas en el mercado peruano e internacional.




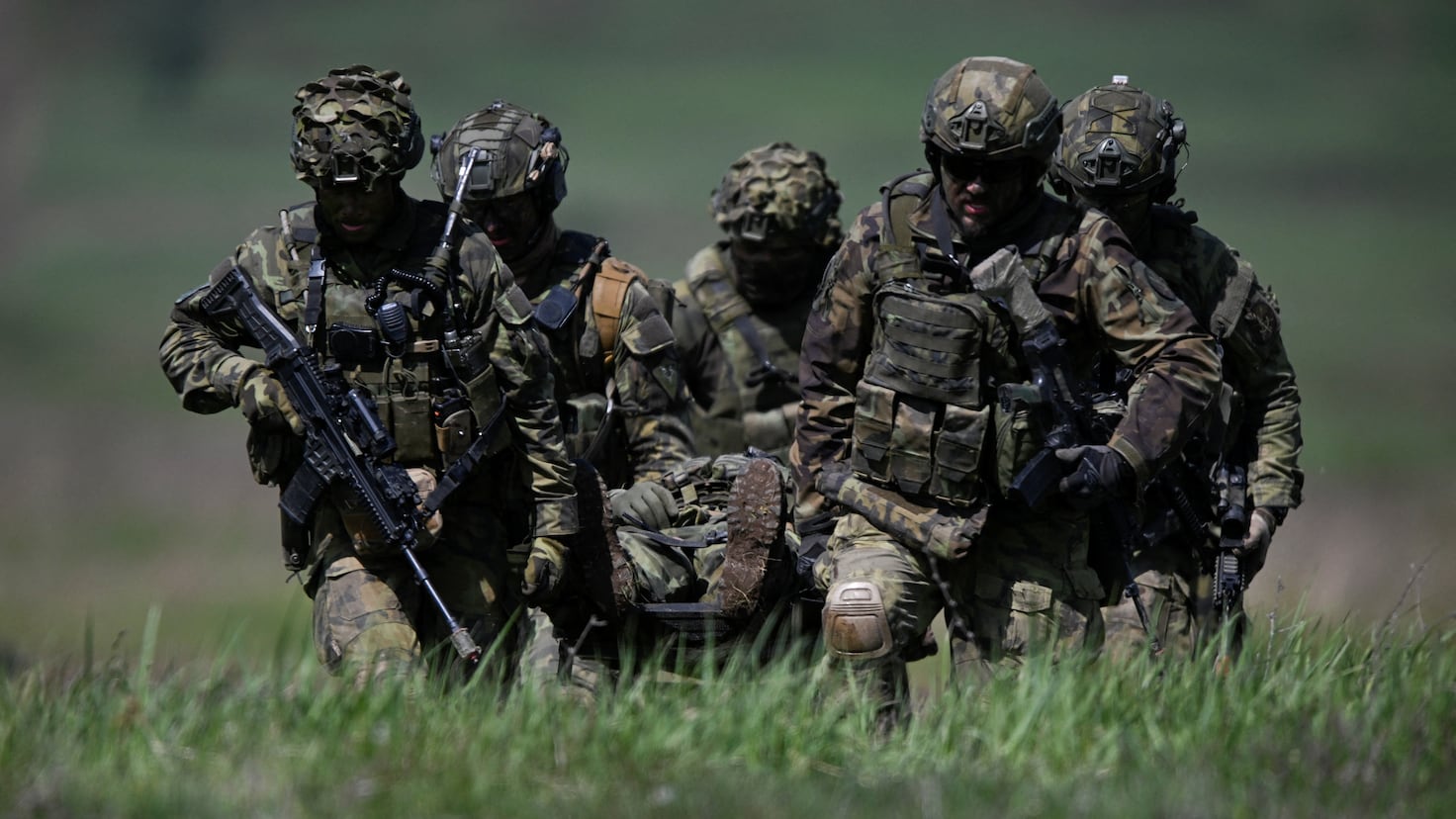
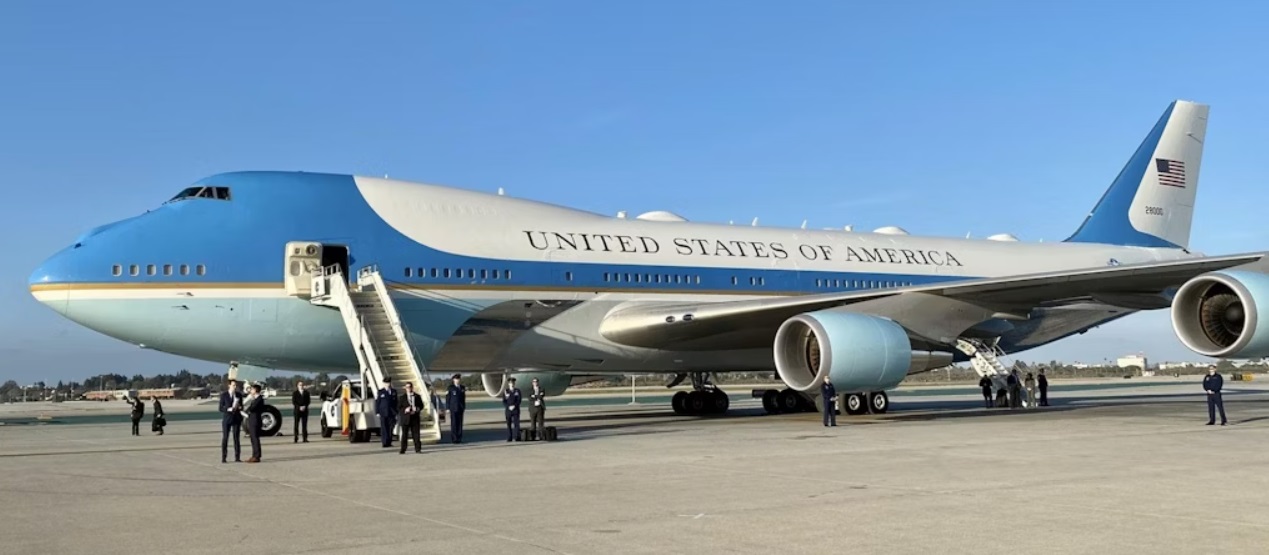
The recent endorsement by the full Peruvian Congress for the entry of U.S. military personnel in the context of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Economic Forum has sparked widespread debate in Peruvian society. The approval was made by a decisive majority, with 62 votes in favor, 24 against, and 7 abstentions. This event marks a milestone in military cooperation between Peru and the United States, in a context where security and logistics are vital for the success of the international event scheduled for November 2024. The resolution authorizes the arrival of at least 600 members of the U.S. armed forces, who will be deployed in various Peruvian cities, such as Lima, Pisco, and Chiclayo, from November 4 to 24. The measure has been justified by the need to ensure the safety of the leaders of the 21 largest economies in the world, who will attend this summit. The chairwoman of the Defense Commission of Parliament, Adriana Tudela Gutiérrez, defended the decision, emphasizing that military support will ensure that the required security standards for such a large-scale event are met. The details of the resolution include authorization for the entry of high-level weapons and equipment, ranging from B-747-200B airplanes to Black Hawk MH-6 helicopters. This has raised concerns in some sectors, who question the necessity of such a military deployment and the potential impact on national sovereignty. However, the government has responded that collaboration with the United States is essential to manage the logistical complexities that an event of this magnitude entails. The arrival of U.S. troops not only implies an increase in security but also brings a series of diplomatic and political implications. With President Joe Biden yet to confirm his attendance, the military presence is interpreted as an attempt to strengthen bilateral relations and demonstrate the United States' commitment to security and stability in the region. However, the measure has drawn critical voices warning about the risks of militarization in a country that has faced tensions due to foreign intervention in the past. Opponents argue that the presence of U.S. military forces could be seen as a violation of national sovereignty and a step towards greater dependence on U.S. foreign policy. Prime Minister Gustavo Adrianzén has spoken out on the situation, indicating that security is a priority and that confirmations regarding the visit of international leaders are made within the confidentiality required for such meetings. This statement highlights the complexity of diplomatic negotiations and the security measures required for events with such a large influx of dignitaries. Additionally, the resolution also allows the Executive Branch to modify the start dates of military support activities if necessary, suggesting that security conditions may change based on the situation at the time. This introduces an element of uncertainty that could influence the country's preparation for the event. Despite the majority support in Congress, the decision to authorize the entry of U.S. troops raises questions about the balance between security and national autonomy. As the date of APEC approaches, it will be crucial to observe how events unfold and what impact this military collaboration will have on public perception and Peru's international relations. In conclusion, the entry of U.S. military personnel in the context of APEC 2024 symbolizes not only an act of international cooperation but also a call for reflection on the implications of such a decision. As the country prepares to host world leaders, security and sovereignty remain fundamental pillars of public and political discussion in Peru.
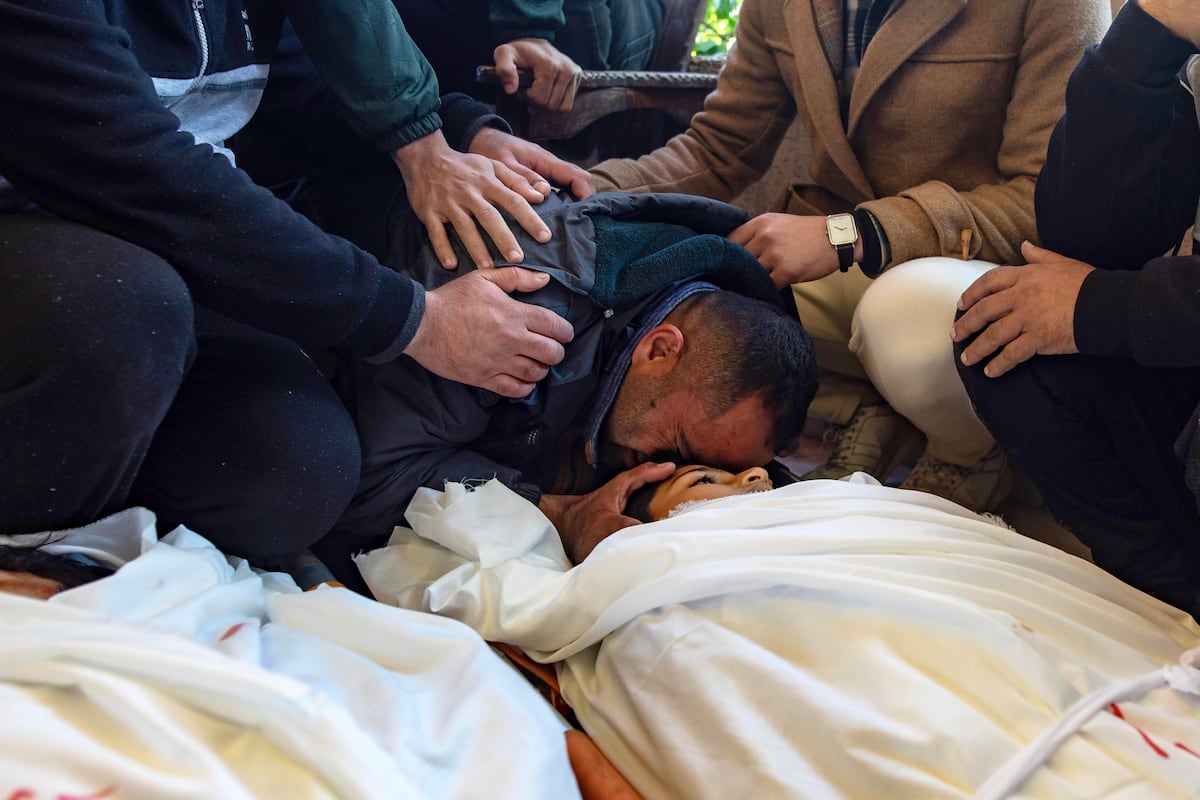
Humanitarian Crisis In Gaza After Israeli Airstrike Leaves 11 Dead And Rising Tensions.
Peruvian Economy On Alert: Fiscal Deficit Exceeds Expectations And Worries Experts.

Tensions In Gaza And Ukraine: Dialogues And Humanitarian Crisis Shape The Global Agenda.


